Exploring the Evolution of Civil Service Reform
Civil service reform has been a cornerstone of government transformation for decades, and for good reason. As someone who has worked in municipal government and nonprofit management, I’ve seen how the right policies can enhance public services and improve the lives of communities. My experience leading community planning initiatives has reinforced a truth that all of us in public administration know: good governance is the foundation of a thriving, equitable society.
Today, civil service reform is more relevant than ever. With increasing public expectations, rapid technological change, and challenges like workforce diversity and aging demographics, the need for ongoing reform is clear. Understanding where we’ve come from and where we’re headed is essential for everyone—from policymakers to public servants and the citizens we serve.
At its heart, civil service reform is about building trust between governments and the people they serve. It ensures that public institutions operate efficiently, equitably, and transparently. By addressing systemic inefficiencies and embracing innovative solutions, civil service reform provides a path for governments better to meet the needs of a diverse and evolving society. Whether modernizing hiring practices or integrating advanced technology, reform efforts are critical to ensuring public institutions remain effective and adaptable in the 21st century.

The Historical Context of Civil Service Reform
Civil service reform in the United States traces back to the Pendleton Civil Service Act of 1883, a landmark shift that ended the patronage-driven “spoils system.” Instead of hiring based on political connections, this act introduced a merit-based system to ensure competence and impartiality in public service.
As the system evolved, additional reforms such as the Hatch Act of 1939, which limited the political activities of civil servants, and the Civil Service Reform Act of 1978, which aimed to modernize the federal workforce, continued to shape the landscape. These efforts were pivotal in creating a framework of fairness, accountability, and efficiency that underpins civil service today.
Yet, the system remains a complex web of federal, state, and local policies, requiring constant evaluation and adjustment to meet modern challenges.
Modern Challenges Facing Civil Service
Having worked with diverse teams and community stakeholders, I’ve observed many issues that civil service reform seeks to address. These include:
- Aging Workforce: Many seasoned public servants are nearing retirement, and attracting young, talented professionals is a critical priority.
- Technology Integration: The digital age has transformed how governments operate, demanding new skills and adaptability from public servants.
- Workforce Diversity: Ensuring equitable representation is not just a goal—building trust and understanding within the communities we serve is necessary.
- Political Polarization: Increasing partisanship makes bipartisan reform efforts challenging, often slowing progress.
- Bureaucratic Inefficiencies: Outdated systems and processes can create barriers to effective governance, something I’ve seen firsthand in municipal operations.
These challenges aren’t insurmountable but require strategic solutions, collaboration, and the willingness to embrace innovation.
Civil Service Reform Today: Key Developments
To address these challenges, reforms at various levels of government are focusing on:
- Meritocracy: Prioritizing merit-based hiring, performance evaluations, and promotions to ensure fairness and competence.
- Streamlining Processes: Technology-driven solutions are being implemented to reduce red tape, improve service delivery, and increase transparency.
- Flexible Work Policies: Remote work and flexible scheduling are emerging as tools to attract and retain talent in an increasingly competitive labor market.
- Anti-Discrimination Measures: Diversity, equity, and inclusion are being emphasized through hiring practices and management training.
- Public Accountability: Whistleblower protections and ethics training enhance trust and integrity within public institutions.
These initiatives reflect a commitment to keeping public service relevant and effective, even as societal needs evolve.
The Role of Technology in Civil Service Reform
Technology has been a game-changer in civil service reform, something I’ve experienced while implementing digital tools for community engagement. From AI-driven recruitment platforms to online training programs, technology is streamlining operations and making services more accessible. Open data initiatives, for example, allow citizens to hold governments accountable while fostering trust.
That said, there are challenges. Cybersecurity risks, bridging the digital divide, and protecting data privacy require careful navigation to avoid unintended consequences.
Why Civil Service Reform Matters
Civil service reform isn’t just a professional concern—it’s deeply personal. Effective reform leads to stronger public trust, more efficient use of taxpayer dollars, and equitable delivery of essential services. I’ve seen how improvements to governance can directly enhance community well-being, from better infrastructure planning to expanded public health programs.
Reform matters because it ensures that government remains accountable, adaptable, and aligned with the needs of its people.
The Future of Civil Service Reform
Looking ahead, I believe the focus will remain on creating a skilled, diverse, and adaptable workforce. Reforms must include expanded training opportunities, more significant support for mental health and wellness, and the integration of cutting-edge technology to improve service delivery.
Equally important is fostering collaboration between policymakers, public servants, and private sector experts. The challenges we face require solutions that draw from the expertise and innovation of multiple sectors.
Shaping the Future of Public Service
Civil service reform is about more than just improving systems—it’s about ensuring that public service remains a force for good in society. As someone who has spent years working in government and nonprofit spaces, I’ve seen how reform can strengthen communities and build a better future for everyone.
Addressing workforce diversity, technological advancements, and evolving societal needs will require creativity, determination, and a shared commitment to excellence. By staying informed and engaged, each of us can play a role in shaping the public service of tomorrow.
Citations
- U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO). “High-Risk Series: Key Issues to Address in Civil Service Reform.”
https://www.gao.gov - Pew Research Center. “America’s Public Workforce: Aging and Increasingly Diverse.”
https://www.pewresearch.org - NASPAA (Network of Schools of Public Policy, Affairs, and Administration). “Recommendations for Public Service Education.”
https://www.naspaa.org - Congressional Research Service. “Civil Service Reform: Historical Context and Modern Challenges.”
https://crsreports.congress.gov
Enhance Your Career with Public Service Certifications
When I started working in public service, I quickly realized that having the right qualifications could make all the difference. While passion and dedication were essential, top certifications for public service professionals provided the credibility and skills I needed to tackle more significant responsibilities and complex challenges. These credentials validated my expertise, gave me confidence, and opened doors to opportunities I hadn’t considered.
Public service is a dynamic and evolving field that demands a balance of technical expertise, strategic thinking, and ethical leadership. Top certifications for public service professionals bridge professional aspirations and real-world impact, equipping individuals with the tools to navigate the complexities of governance and administration. Whether you’re new to the field or a seasoned professional, the proper certifications can sharpen your skills, broaden your perspective, and position you as a trusted leader in the eyes of your colleagues and the community.
Certifications are pivotal in public service because they validate skills, enhance expertise, and unlock new opportunities. From public administration certifications to civil service exams, these credentials cater to a wide range of roles across the public service spectrum. They lead to career advancement and equip professionals with the knowledge to deliver impactful and efficient governance.

Why Certifications for Public Service Matter
Certifications for public service go beyond adding credentials to your résumé—they signify dedication, expertise, and a commitment to professional growth. These certifications validate specialized skills for effective governance and efficient public service delivery. They also foster public trust by ensuring adherence to ethical standards and regulatory requirements.
For me, earning my first certification in public service felt like a significant milestone. It showed my peers and supervisors I was committed to my career and equipped to handle greater responsibilities. This recognition often translates into higher job satisfaction, as certifications align your skills with your career goals. Moreover, certifications for public service provide a critical edge in today’s competitive job market, making them a key factor in promotions and leadership opportunities.
Public Administration Certification: A Leadership Foundation
Pursuing a Public Administration Certification is transformative for public service professionals. This certification equips individuals with essential skills in management, policy development, and ethical decision-making. For example, I recall how this training enabled me to craft policies emphasizing transparency and accountability, which were pivotal in gaining community trust during a challenging time in my city.
Public Administration Certifications are a cornerstone for aspiring leaders, empowering them to tackle complex challenges with innovative solutions. They also foster strategic thinking that drives impactful governance, making them invaluable for public service professionals.
Civil Service Exams: Your Gateway to Government Roles
Civil service exams are often the first step for individuals pursuing government roles. I remember the mix of excitement and nerves when preparing for my exam. Developing structured study schedules and practicing with mock tests were crucial strategies that helped me succeed.
These exams assess core competencies and ensure that candidates meet the high standards required for public service roles. Successfully passing a civil service exam opens the door to rewarding careers in government and provides the opportunity to make meaningful contributions to public welfare.
Top Certifications to Advance Your Public Service Career
Certifications tailored to specific public service roles offer specialized knowledge and career advancement opportunities. Some of the most impactful certifications include:
- Certified Public Manager (CPM): Focuses on leadership and management skills, preparing participants for senior roles in the public sector.
- Certified Government Financial Manager (CGFM): Emphasizes fiscal accountability and expertise in government financial processes.
- Certified Emergency Manager (CEM): Equips professionals with the tools for disaster preparedness and crisis management.
- National Certified Investigator/Inspector Training (NCIT): Ideal for those in regulatory compliance and investigative roles.
- Certified Nonprofit Professional (CNP): Strengthens nonprofit governance, fundraising, and operational management skills.
Each certification highlights a professional’s dedication to their field, enhances their credibility, and provides opportunities for career growth.
The Benefits of Earning Public Service Certifications
Earning certifications offers numerous advantages. They often serve as the key to promotions and leadership roles, validating a professional’s expertise and enhancing credibility with colleagues and the public. Certification programs also create networking opportunities, connecting professionals with peers and mentors who can guide them toward new career paths.
From my experience, certifications encourage continuous learning. Staying updated on trends and best practices in the field makes you more effective in your role and keeps your work engaging and fulfilling.
Preparing for Certification Exams
Preparing for certification exams requires a strategic approach. I found it helpful to break down the material into manageable sections and create a study schedule that fit my routine. Practicing with mock exams helped me become familiar with the test format and boosted my confidence.
Study groups were another invaluable resource—discussing complex topics with peers often led to deeper understanding and new perspectives. These preparation strategies can make all the difference in achieving success.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
Public service professionals must adapt to evolving policies and technologies. Continuing education through workshops, seminars, and online courses provides valuable insights into emerging trends and enhances expertise.
I recently attended a public policy data analysis workshop, which broadened my skill set and helped me connect with other professionals in my field. These learning opportunities contribute to certifications or recertifications, reinforcing a commitment to professional growth and excellence.
Certifications as Career Catalysts
Certifications are potent tools for public service professionals, offering enhanced skills, career advancement, and increased credibility. They help individuals stand out in their field, build public trust, and contribute to effective governance.
By investing in professional development through certifications, public service professionals enhance their career prospects and play a vital role in delivering better outcomes for their communities.
Exploring the Essential Skills and Qualities of Healthcare Leadership
Health care administrators are pivotal in shaping the success of healthcare organizations, driving operations, and ensuring exceptional patient outcomes. Mastering the leadership skills needed as a health care administrator goes beyond managing resources; these professionals influence team dynamics, promote patient safety, and adapt to the ever-evolving healthcare industry. Administrators must develop a broad skill set that combines technical expertise with emotional intelligence and strategic thinking to thrive in this demanding role.
Many leadership skills required for healthcare administrators also apply to Public Health Administrators, who manage programs and policies promoting community health. These professionals balance strategic oversight with hands-on implementation, often addressing broader public health challenges such as disease prevention, health equity, and emergency preparedness. Whether you’re interested in hospital administration or public health leadership, mastering these core skills is vital for ensuring meaningful and measurable impact.
According to the American College of Healthcare Executives (ACHE), effective healthcare leaders demonstrate competencies in communication, relationship management, professionalism, and knowledge of the healthcare environment. These competencies are crucial for administrators who aim to lead their organizations successfully.
In his book, Leadership in Healthcare: Essential Values and Skills, Carson F. Dye emphasizes the importance of developing a core set of values that drive actions during challenging times. He identifies essential values that highly effective leaders possess and describes their behaviors. This perspective underscores the significance of aligning personal values with leadership practices in healthcare settings.
For those aspiring to leadership roles in healthcare or pursuing degrees like a Master of Public Administration (MPA) with a healthcare focus, understanding the essential skills of a hospital administrator or Public Health Administrator is the first step toward professional success. By cultivating these leadership traits, professionals can position themselves to make a meaningful impact on healthcare organizations and the communities they serve.

1. Strategic Planning
One of the most critical skills for a hospital administrator is strategic planning. This involves setting organizational goals, allocating resources, and designing actionable plans that align with patients and the community’s needs. Strategic planning helps administrators address rising costs, workforce shortages, and shifting patient demographics in the dynamic healthcare industry.
Effective healthcare leaders anticipate trends, analyze data, and collaborate with team members to craft forward-thinking solutions. They ensure that healthcare facilities are reactive and proactive, enabling sustainable growth and improved care delivery.
2. Communication Skills
Clear communication is essential in any healthcare setting. Administrators must effectively convey complex information to staff, stakeholders, and patients, ensuring everyone understands policies, procedures, and objectives. Strong communication builds trust, fosters collaboration, and ensures alignment across departments.
Soft skills, such as active listening and empathy, are equally important. These skills enable administrators to address concerns, provide constructive feedback, and maintain positive relationships with team members and patients. Emotional intelligence, a hallmark of effective leadership, enhances communication by helping leaders navigate interpersonal dynamics with sensitivity and professionalism.
3. Financial Management
Navigating budgets, managing expenses, and ensuring fiscal responsibility are vital components of hospital administration. In the United States, where healthcare costs are a significant concern, administrators must balance financial constraints to deliver high-quality care.
Strong financial management involves analyzing financial data, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and making informed decisions that align with organizational goals. Leaders in healthcare facilities must also comply with federal and state regulations and ensure that financial practices meet legal standards.
Administrators pursuing professional development through programs like an MPA in Finance and Budgeting can build expertise in managing resources effectively, ensuring long-term organizational sustainability.
4. Problem Solving and Decision-Making
Administrators often face complex problems that require innovative solutions, such as managing staffing shortages or responding to public health emergencies. Strong problem-solving skills and the ability to make data-driven decisions are essential in these scenarios.
Effective leaders evaluate multiple options, anticipate potential challenges, and choose the best action based on evidence and team input. Their ability to make sound decisions directly impacts patient safety and operational efficiency in high-stakes situations.
5. Team Leadership and Collaboration
A thriving healthcare administrator fosters a cohesive, motivated team that works together to achieve shared goals. Leaders in this field must inspire trust, resolve conflicts, and promote inclusivity, creating an environment where every team member feels valued.
Collaboration is key to navigating the complexities of healthcare organizations. Administrators must work across disciplines, uniting physicians, nurses, and support staff to deliver exceptional care. By encouraging collaboration and open communication, administrators can build a workplace culture prioritizing employee satisfaction and patient outcomes.
6. Adaptability and Innovation
The healthcare industry is constantly changing, shaped by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and patient needs. Administrators must remain adaptable, embracing change as an opportunity for growth and improvement.
Effective leaders champion innovation by adopting new technologies, such as electronic health records (EHR) and telemedicine platforms, to streamline operations and enhance care delivery. They also develop professionally and stay informed about emerging trends and best practices in healthcare administration.
By fostering a culture of innovation and continuous improvement, leaders position their organizations to thrive in a competitive and dynamic environment.
Characteristics of a Leader in Healthcare
Successful healthcare administrators share several key characteristics that set them apart. These include:
- Visionary Thinking: The ability to see the big picture and guide the organization toward long-term goals.
- Resilience: Remaining calm and focused under pressure while navigating challenges.
- Empathy: Understanding and addressing the needs of patients, staff, and stakeholders.
- Integrity: Upholding ethical standards and fostering trust within the organization.
These traits and technical expertise enable administrators to lead confidently and purposefully, ensuring that their healthcare organizations deliver high-quality care and achieve operational excellence.
Building a Leadership Role in Healthcare
Advanced education and certifications are valuable for those aspiring to become healthcare leaders. Degrees such as a Master of Public Policy (MPP) or an MPA with a healthcare specialization provide in-depth policy analysis, financial management, and strategic planning training.
Certifications in healthcare administration can also enhance career prospects, validating expertise in areas such as risk management, patient safety, and organizational leadership. Aspiring administrators can prepare to take on leadership roles in hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare settings by investing in their education and skill development.
Why Leadership Qualities Matter in Healthcare
In the high-stakes world of healthcare, strong leadership directly impacts patient care, employee satisfaction, and organizational success. Administrators with the right leadership qualities can:
- Improve Care Delivery: Streamlining processes to enhance patient experiences and outcomes.
- Promote Patient Safety: Implementing systems and protocols that reduce errors and ensure quality care.
- Drive Organizational Efficiency: Managing resources effectively to achieve operational goals.
Leaders prioritizing these outcomes create a ripple effect, fostering positive change within their organizations and the broader community.
Supporting Healthcare Facilities Through Leadership
Healthcare facilities rely on administrators to balance competing priorities, from financial constraints to workforce challenges. By developing a comprehensive skill set, leaders can confidently navigate these complexities and ensure that their facilities remain responsive to patients’ and staff’s needs.
For instance, administrators working in underserved areas may focus on expanding access to care, while those in large urban hospitals might prioritize adopting new technologies to enhance operational efficiency. In either case, effective leadership is the driving force behind sustainable success.
Becoming an Effective Healthcare Leader
For aspiring healthcare administrators, the journey begins with a commitment to lifelong learning and skill development. Whether through advanced degrees, certifications, or on-the-job experience, building expertise in hospital administration skills, financial management, and strategic planning is essential.
Programs like an MPA or MPP provide the foundational knowledge needed to excel in leadership roles, while hands-on experience hones the interpersonal and decision-making skills critical to success. By cultivating the proper leadership role and investing in their professional development, future administrators can make a lasting impact in the healthcare industry.
Conclusion: Leading the Future of Healthcare
Healthcare administrators are more than managers—visionaries guiding their organizations toward success. By mastering essential skills such as strategic planning, communication, financial management, problem-solving, team leadership, and adaptability, they can confidently navigate the complexities of the healthcare industry.
Aspiring leaders should prioritize developing these hospital administration skills while pursuing advanced education and certifications. With the right preparation, they can become effective healthcare leaders who drive meaningful change, improve patient outcomes, and ensure the success of their healthcare organizations.
Citations
- American College of Healthcare Executives. “Characteristics of Effective Healthcare Leadership.”
https://www.ache.org - National Institutes of Health. “Leadership in Health Care Organizations: Principles and Practices.”
https://www.nih.gov
World Health Organization. “Building Leadership Capacity in Healthcare.”
https://www.who.int
Exploring The Vital Role of FAC-P/PM Certified Professionals
Program and project managers are the backbone of federal government operations. They ensure initiatives are completed efficiently, on budget, and aligned with strategic goals. The Federal Acquisition Certification for Program and Project Managers equips professionals with the skills and knowledge to lead complex programs, deliver meaningful outcomes, and effectively serve the public.
Drawing from my experience managing community-driven initiatives, I’ve seen firsthand how effective project management can transform ideas into impactful results. For those pursuing careers in government or exploring advanced credentials for project management, this certification provides a structured pathway to success while addressing the unique challenges of managing federal programs.
Government Program Managers play a pivotal role in translating policy into action. They oversee federal initiatives that address critical public needs, such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. These professionals are vital in ensuring public programs meet their objectives by managing budgets, coordinating with diverse stakeholders, and evaluating outcomes. With their work bridging strategy and execution, these managers rely heavily on structured training programs, such as the Federal Acquisition Certification, to refine their skills and deliver results that benefit communities nationwide.
In this article, we’ll explore what FAC-P/PM certification is, why it matters to federal operations, the distinct levels within the program, and the steps required to earn this prestigious credential. Whether you’re a current program manager or aspiring to join the federal workforce, understanding this certification can be the key to unlocking your potential and advancing your career.

What Is This Certification?
The Federal Acquisition Certification for Program and Project Managers is a government-mandated credential designed to standardize and enhance the skills of professionals overseeing federal initiatives. It ensures that managers possess the technical, leadership, and business acumen to manage projects effectively from inception to completion.
This certification is specifically tailored to meet federal standards. While credentials like the Project Management Professional (PMP) are globally recognized, this program focuses on equipping managers with skills uniquely suited to the public sector. Professionals in these roles must navigate regulatory complexities, limited resources, and diverse stakeholder needs.
Why This Certification Matters
This credential is a cornerstone for developing skilled professionals capable of leading federal programs and projects with precision and accountability. Federal initiatives often involve significant investments, intricate regulations, and complex stakeholder dynamics. Ensuring these projects are managed effectively is not just a matter of efficiency—it’s a public trust. This program provides a robust framework that equips managers with the competencies to navigate these challenges while achieving measurable results.
Professionals with this certification bring consistency and expertise to their roles, helping agencies meet organizational objectives while maintaining compliance with stringent federal standards. The program’s emphasis on standardization ensures that certified managers adhere to proven practices that align with acquisition regulations, fostering a uniform approach across agencies.
The certification emphasizes technical skills, leadership, and critical decision-making capabilities in public service. Certified professionals learn to allocate resources effectively, evaluate risks, and implement strategies that optimize project outcomes. This combination of technical knowledge and leadership acumen positions certified managers as indispensable assets in achieving project success and driving innovation.
Certification Levels
Each level of FAC-P/PM certification—entry, mid, and senior—builds on the previous one and focuses on progressively advanced skills. For instance, entry-level training emphasizes foundational competencies, while senior levels prepare professionals to lead large-scale programs.
The certification focuses on three core levels:
- Entry-Level: For beginners managing simple projects or contributing to more extensive programs.
- Mid-Level: For those managing complex projects with significant operational or financial impact.
- Senior-Level: For experienced professionals leading large-scale programs and driving high-level organizational strategies.
Each level emphasizes key competencies such as strategic planning, risk management, stakeholder engagement, and performance evaluation, ensuring certified professionals are well-prepared to lead effectively.
Earning the Certification
To earn a certificate in FAC-P/PM, professionals must meet the certification requirements, including completing structured FAC-P/PM training and demonstrating expertise in key areas like acquisition planning and financial management.
Career Growth Opportunities
Earning this credential opens doors to high-impact public administration and program management careers. It prepares professionals to:
- Oversee federal projects and programs effectively, ensuring strategic alignment with agency objectives.
- Collaborate with stakeholders, including government officials, contractors, and community organizations, to achieve common goals.
- Manage project teams and resources efficiently while navigating regulatory requirements.
- Develop strategies for achieving long-term success in public sector initiatives.
Professionals who obtain this certification demonstrate mastery of leadership, risk assessment, and organizational strategy. The program complements educational paths such as a Master of Public Administration (MPA) or Master of Public Policy (MPP), enhancing job opportunities and providing a competitive edge in securing federal management positions.
Key Components of Training
The training program focuses on essential competencies for federal managers, such as financial management, risk mitigation, and stakeholder collaboration. FAC-P/PM training requirements include modules that teach professionals to ensure project success while maintaining compliance with federal standards. Some providers even offer a free trial to help participants assess the program’s value.
Key areas of focus include:
- Acquisition Planning: Aligning procurement strategies with program goals and ensuring compliance with federal acquisition laws.
- Risk Management: Teaching managers to identify, analyze, and mitigate risks to avoid delays or budget overruns.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Equipping professionals to collaborate with diverse stakeholders to drive alignment and consensus.
- Performance Metrics: Using data-driven insights to evaluate program success and implement necessary adjustments.
These competencies are essential for professionals managing individual projects and large-scale programs in the federal space.
Challenges in Federal Program Management
Managing federal programs and projects comes with its unique set of challenges:
- Budget Constraints: Federal projects often operate under tight budgets, requiring innovative resource allocation strategies.
- Complex Regulations: Navigating the intricate web of acquisition rules and compliance standards can be daunting.
- Stakeholder Expectations: Balancing the diverse needs of government officials, contractors, and the public is critical to ensuring program success.
- Long Timelines: Many federal programs span multiple years, making sustained focus and adaptability essential.
Certified managers are better equipped to address these challenges and ensure their efforts align with long-term agency objectives.
Why Certification Is Worth Pursuing
This credential validates expertise and positions professionals for leadership roles in federal program management. The demand for certified managers continues to grow as the federal government’s operations become increasingly complex.
Professionals who earn this credential gain a deep understanding of the acquisition process, effective resource management, and strategic planning. These skills are crucial for achieving project success and meeting public expectations. For aspiring leaders in public administration, combining this certification with an advanced degree, such as an MPA in Finance & Budgeting or an MPP in Social Policy, provides the tools needed to excel in the field.
Building Federal Leadership
Program and project managers drive progress and ensure that taxpayer dollars are used effectively. Certification equips these professionals with the skills to lead projects confidently, improve outcomes, and support the federal government’s mission to serve the public.
For those looking to advance their careers in federal program management, this certification is an investment that pays off in career growth, enhanced skills, and the ability to make a lasting impact on public service.
Citations
- Office of Federal Procurement Policy. “The Federal Acquisition Certification for Program and Project Managers.”
https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov - Government Accountability Office (GAO). “Best Practices for Federal Program Management.”
https://www.gao.gov
Project Management Institute (PMI). “Federal Project Management and Leadership.”
https://www.pmi.org
Understanding The Roles and Intersections of Public Administration and Public Policy
Public administration and public policy are two critical fields that form the backbone of governance, shaping how governments operate and address societal needs. These disciplines work hand-in-hand to ensure government initiatives are designed effectively and implemented efficiently. However, understanding the distinction between Public Administration vs Public Policy is essential for anyone looking to pursue a career or degree in these areas.
Public administration focuses on managing the day-to-day operations of government and ensuring that public programs and services are delivered effectively. This involves budgeting, personnel management, and overseeing the implementation of policies crafted by lawmakers. Public administrators are the operational leaders who bridge the gap between policy decisions and their real-world application.
On the other hand, public policy centers on creating, analyzing, and evaluating laws and strategies to address societal challenges. Policymakers are responsible for identifying issues, designing evidence-based solutions, and considering their long-term impact on communities. This analytical and strategic work often lays the groundwork for the actions carried out by public administrators.
Whether pursuing a degree in public administration or a public policy MPP, understanding the differences between these fields can help you choose the path that aligns with your goals and career aspirations. Both play essential roles in advancing public service, improving lives, and addressing the complex needs of society.
Both fields play vital roles in public service. Public administration professionals often work behind the scenes to ensure policies are implemented efficiently, resources are allocated effectively, and government programs run smoothly. On the other hand, public policy experts take a broader view, analyzing societal challenges, designing evidence-based solutions, and evaluating the long-term implications of proposed strategies. Their combined efforts help drive progress and create systems that promote equity, sustainability, and public welfare.
Whether pursuing a career in the public sector, working with nonprofit organizations, or collaborating with the private sector, both fields offer meaningful opportunities to make a difference. Public administration equips professionals to lead teams, manage budgets, and oversee operations, ensuring that programs deliver results. Public policy, by contrast, prepares individuals to tackle complex issues such as climate change, healthcare reform, and economic inequality through research and strategic planning. Together, these disciplines form a collaborative foundation for effective governance.
Let’s explore what public policy is, what public administration is, and how the two intersect in governance and public service.
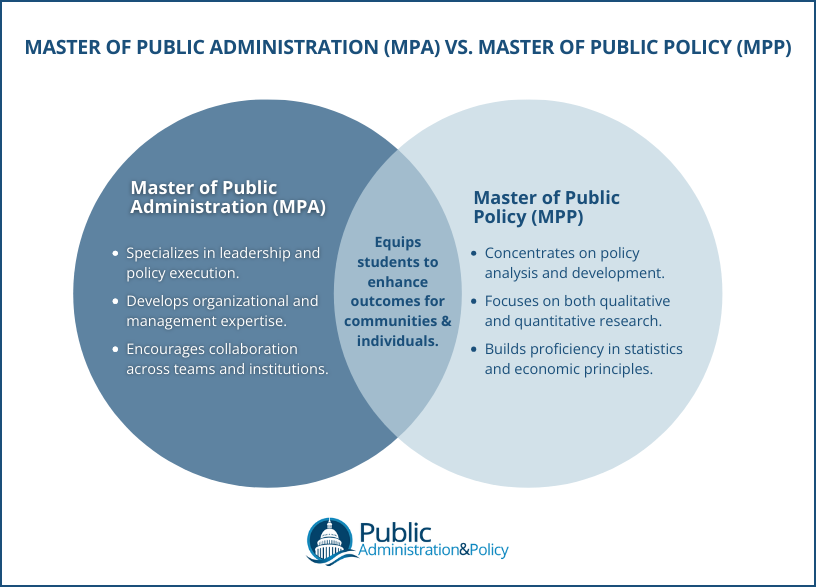
Public Administration vs. Public Policy: Key Differences
Public Administration and Public Policy are complementary yet distinct fields that play vital roles in governance. Understanding the differences between Public Administration vs. Public Policy can help clarify their unique contributions to public service. Public Administration focuses on the operational aspects of implementing programs and managing resources, ensuring that policies translate into actionable outcomes. In contrast, Public Policy emphasizes the strategic design, analysis, and evaluation of laws and strategies that address societal challenges.
These differences influence the work professionals perform, the skills required, the sectors they operate in, and the types of careers they pursue. By examining their distinct focuses and responsibilities, we can better understand how these fields intersect and where they diverge, making it easier to choose a path that aligns with your goals.
| Aspect | Public Administration | Public Policy |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Managing and implementing public programs. | Creating and evaluating laws and strategies. |
| Core Skills | Leadership, budgeting, operations management. | Research, data analysis, and problem-solving. |
| Sectors | Local, state, and federal governments; public sector roles. | Think tanks, school of public affairs, global organizations. |
| Career Examples | City Manager, Public Health Administrator, Budget Analyst. | Policy Analyst, Legislative Aide, Public Policy Consultant. |
For example, while a Public Health Administrator ensures programs to combat disease are effectively implemented, a Policy Analyst evaluates whether those programs achieve desired outcomes.
What Is Public Administration?
Public administration refers to the management and execution of government programs and services, encompassing the day-to-day operations that keep public institutions running smoothly. It focuses on translating the vision of policymakers into actionable programs, ensuring that the laws and strategies crafted by elected officials and policy experts are implemented efficiently and effectively at the local, state, and federal levels.
This field is vital to public service, as it directly impacts how communities receive essential services such as healthcare, education, infrastructure, and public safety. Public administrators oversee budgets, allocate resources, manage personnel, and coordinate with stakeholders to ensure programs meet their objectives. They are problem-solvers who work to address operational challenges while maintaining transparency, accountability, and equity in service delivery.
At its core, public administration is about leadership and public management. Professionals in this field must balance strategic oversight with practical execution, often collaborating with diverse teams, including government agencies, nonprofit organizations, and private sector partners. By ensuring that government programs align with the needs of the public, public administration plays a critical role in improving societal outcomes and fostering trust in public institutions.
Key Features of Public Administration
- Public Management: Overseeing resources, personnel, and operations to achieve policy objectives.
- Service-Oriented: Focused on delivering essential services to citizens through efficient management.
- Collaboration: Works closely with government agencies, nonprofit organizations, and the private sector.
Careers in Public Administration
Professionals in public administration take on critical leadership roles within local government, state agencies, and federal departments, ensuring the effective implementation of policies and programs. These individuals manage operations, oversee budgets, and lead teams to deliver services that address community needs. Their work bridges the gap between policy decisions and tangible outcomes, making them essential to the success of public initiatives.
Typical careers in public administration include:
- City/County Manager: Serves as the chief executive officer for a city or county, overseeing daily operations, budgets, and staff. City and county managers work closely with elected officials to implement policies that align with community goals, addressing infrastructure, public safety, and economic development.
- Public Budget Sector Analyst: Focuses on evaluating government spending and resource allocation to promote fiscal efficiency. Budget analysts analyze financial performance, identify cost-saving opportunities, and provide recommendations to ensure taxpayer dollars are used effectively.
- Public Health Administrator: Leads public health programs and initiatives, addressing community health challenges such as disease prevention, access to care, and emergency preparedness. Public health administrators collaborate with healthcare providers, nonprofit organizations, and government agencies to improve population health outcomes.
- Grant Administrator: Oversees government or nonprofit programs’ grant application, compliance, and reporting process. These professionals ensure that funding is allocated effectively and aligns with organizational goals, enabling critical initiatives to succeed.
- Nonprofit Executive Director: Leads nonprofit organizations by managing strategic goals, fundraising efforts, and program execution. Executive directors work to ensure their organizations achieve their mission while maintaining financial sustainability and accountability.
- Government Program Manager: Manages the planning, executing, and evaluating public programs, often focusing on healthcare, education, or infrastructure. These professionals ensure programs meet their objectives and align with broader policy goals.
A Master of Public Administration (MPA) prepares students for these leadership roles by offering comprehensive training in public management, budgeting, policy implementation, and organizational leadership. Graduates of MPA programs are equipped with the skills to navigate the complexities of public sector leadership, making them valuable assets to governments, nonprofits, and private organizations collaborating with the public sector.
What Is Public Policy?
Public policy involves creating, analyzing, and evaluating strategies to address complex societal challenges. It identifies issues affecting communities, develops evidence-based solutions, and implements strategies to achieve specific goals. This field emphasizes research, critical thinking, and problem-solving, providing the foundation for laws, regulations, and programs that guide how governments, organizations, and societies function.
Public policy is inherently interdisciplinary, drawing on economics, political science, sociology, and public health to craft well-rounded solutions. Professionals in this field conduct in-depth research to understand the root causes of problems, gather data to assess the effectiveness of potential strategies and consult with stakeholders to ensure that policies are equitable and practical.
Whether addressing local issues such as housing and transportation or tackling global challenges like climate change and international security, public policy plays a critical role in shaping the future. By prioritizing the public good and balancing diverse interests, policymakers work to create sustainable, long-term solutions that enhance the quality of life for individuals and communities.
Key Features of Public Policy
- Analytical Focus: Examines societal issues to craft effective solutions.
- Long-Term Impact: Aims to create sustainable policies that address complex challenges.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Involves collaboration across economics, criminal justice, and environmental science fields.
Careers in Public Policy
Professionals in public policy play a pivotal role in shaping the laws, regulations, and programs that address societal challenges. They often work in diverse settings, including think tanks, government agencies, nonprofit organizations, and consulting firms. These roles require strong analytical, research, and communication skills to develop solutions that promote equity, sustainability, and public well-being.
Some popular careers in public policy include:
- Policy Analyst: Researches and evaluates the effectiveness of public programs and policies, using data-driven insights to recommend improvements. Policy analysts work on issues ranging from healthcare reform to economic development, contributing to informed decision-making for governments, nonprofits, and private organizations.
- Environmental Policy Advisor: Focuses on creating and advocating for policies that address climate change, conservation, and renewable energy. These professionals collaborate with governments, NGOs, and private sector stakeholders to promote sustainable practices and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Urban Policy Planner: Design strategies to enhance urban development and infrastructure, addressing challenges like housing shortages, public transit, and community sustainability. Urban policy planners work closely with local governments and community organizations to create livable, equitable, and efficient cities.
- Public Policy Consultant: Advises governments, businesses, and nonprofits on developing and implementing effective policies. Consultants often specialize in fields such as healthcare, education, or economic development, providing tailored strategies to achieve specific objectives.
- Think Tank Analyst: Conducts in-depth research on public policy issues, generating evidence-based recommendations for improving governance and addressing societal problems. Think tank analysts influence decision-making by publishing reports, hosting forums, and engaging with policymakers.
With a degree in public policy, such as a Master of Public Policy (MPP), professionals are well-prepared to tackle these roles. They gain the expertise to analyze complex issues, design innovative strategies, and implement solutions that make a meaningful difference in communities and beyond.n data analysis, economics, and policy design, preparing them to tackle pressing issues in the United States and beyond.
The Intersection of Public Administration and Public Policy
Though distinct, public administration and public policy are deeply interconnected, forming a continuous cycle of strategy and execution. Policies crafted by public policy analysts provide the framework for addressing societal challenges, but their success depends on the practical implementation by public administrators. At the same time, the insights and challenges encountered during implementation often shape and refine future policymaking efforts, ensuring policies remain relevant and impactful.
For example, a public policy expert might design a strategy to improve affordable housing access. Public administrators then lead in implementing that strategy, coordinating with local governments, community organizations, and developers to bring the policy to life. If obstacles arise—such as funding shortages or regulatory hurdles—these challenges can inform revisions to the policy, creating a feedback loop that enhances its effectiveness over time.
This dynamic relationship underscores the importance of collaboration between policymakers and administrators. By working together, they ensure that public programs are both visionary and practical, addressing immediate needs while laying the foundation for sustainable, long-term solutions. Whether tackling issues like healthcare reform, environmental protection, or infrastructure development, the intersection of public administration and public policy drives meaningful progress in governance and public service..
Examples of Collaboration
Affordable Housing: A Public Policy Consultant develops a comprehensive housing program to increase access to affordable living options. A Community Development Specialist collaborates with local governments, nonprofit organizations, and developers to implement the program, ensuring that funding, zoning regulations, and community needs align for successful execution.
Environmental Regulations: Policymakers design air quality standards to reduce pollution and protect public health. Public administrators enforce these regulations by conducting inspections, monitoring compliance, and engaging with industries to promote environmentally responsible practices. Their efforts ensure the policy’s intended impact is realized at the local and state levels.
Public Health Initiatives: A policy expert creates strategies to improve healthcare access for underserved populations. Public Health Administrators take these strategies and put them into action by overseeing vaccination programs, expanding clinic availability, and coordinating with healthcare providers to address community health needs effectively.
These examples highlight the interconnected roles of public administration and public policy. Policymakers craft strategies that address societal challenges, while administrators translate those strategies into actionable programs. Together, they ensure that public initiatives achieve their intended goals, with public administration serving as the engine that drives policies forward.
Preparing Students for Public Service
Advanced education is crucial for careers that bridge Public Administration vs Public Policy. A public administration degree, such as an MPA, equips students with leadership and operational skills for managing programs and budgets. Conversely, an MPP degree program focuses on policy analysis and strategy development, making it ideal for roles in policymaking or advocacy.
Schools like NASPAA-accredited programs ensure students gain the practical and theoretical knowledge needed to excel in both fields. These programs emphasize collaboration, critical thinking, and innovation, preparing students to address the complexities of modern governance while navigating the relationship between Public Administration vs Public Policy effectively.
Bridging Strategy and Execution in Public Service
Public Administration vs Public Policy represents two sides of the same coin, working together to improve societal well-being. Public administrators ensure that programs and services run smoothly, while policymakers focus on creating strategies to guide those efforts.
Whether you’re drawn to the operational focus of public administration or the analytical depth of public policy, both fields offer opportunities to make a lasting impact. By pursuing an MPA program, a public policy MPP, or another degree program, you can develop the skills and expertise needed to lead in the public sector, collaborate with government agencies, and drive meaningful change at the local, state, and federal levels.